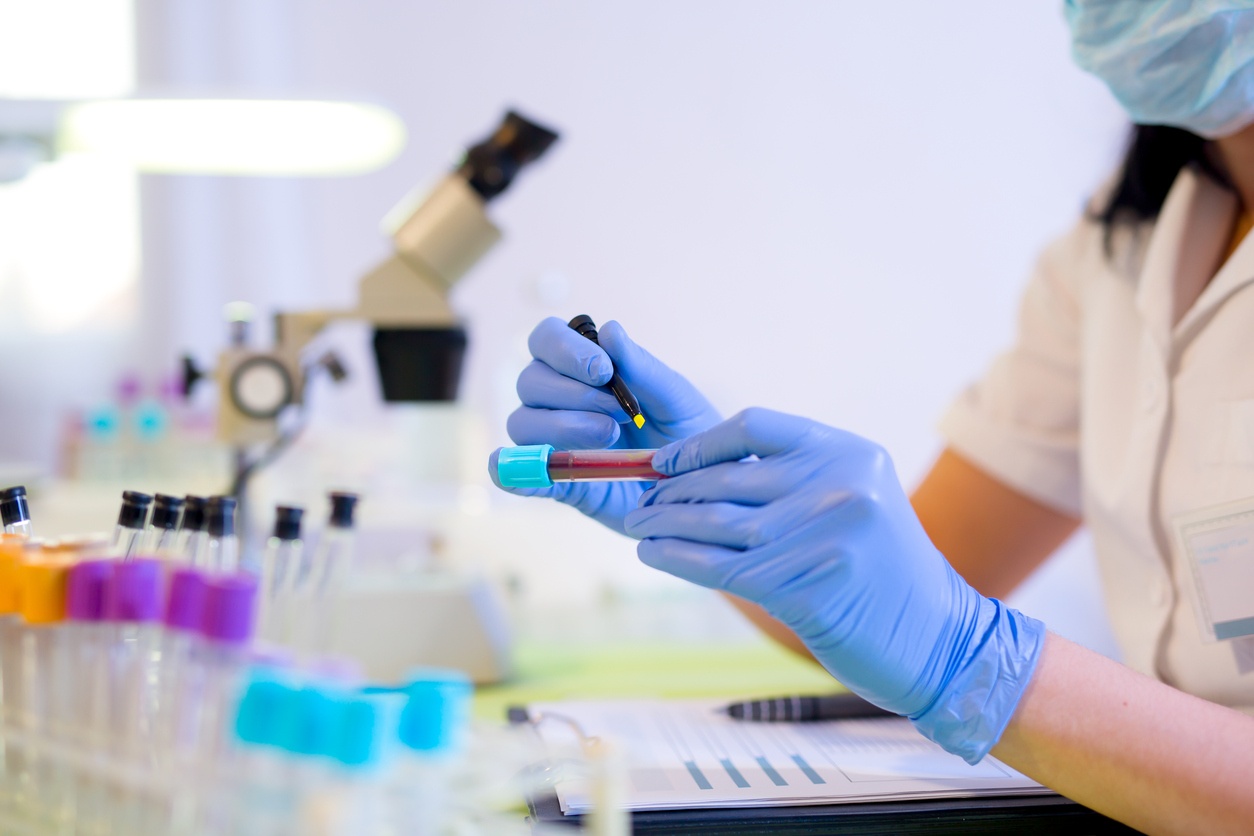
Phlebotomy is the surgical puncturing of a vein to collect and draw blood, whether for laboratory tests or blood donation. Employment in this healthcare profession is projected to grow 25 percent through 2026. The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) projects that demand will remain high in this job as doctors and other healthcare professionals require blood work for analysis and diagnosis.
The World Health Organization (WHO) offers comprehensive best practices for phlebotomy. Here are some highlights for educators, with links at the bottom of the article for the complete book chapter.
Blood Draws
All staff in a clinic responsible for blood draws and handling should be properly educated in phlebotomy. Phlebotomists usually have an associate degree or similar certification stemming from classroom learning and on-the-job experience. Some phlebotomy students benefit from a bachelor’s degree in medical technology.
Teach students that best practices involve the following:
- Planning ahead – Collect equipment needed for the procedure, and place it within easy reach, making sure all items are clearly visible.
- Using an appropriate location – A phlebotomist should work in a quiet, clean, and well-lit area, properly equipped with supplies and furniture needed for efficiency, as well as patient comfort and safety. Setting up a simulated room to demonstrate this is ideal.
- Quality control – In order to prevent mishaps, teach students appropriate quality assurance elements including but not limited to: education, standard operating procedures (SOPs), identification procedures to ensure they have the right patient, condition of the sample, safe transportation, and an incident reporting system. Quality control is an excellent area for simulation scenarios and role-playing to assist students to learn these elements.
- Standards for quality care for patients and healthcare workers – More details on this below.
- Quality laboratory sampling – Instruct on proper labeling, transportation, and needle usage to ensure the highest quality and accuracy of laboratory results.
Quality Care for Patients and Health Workers
To improve safety standards for patients and healthcare workers, it is also important to teach the following:
- Appropriate supplies and protective equipment – Hand-hygiene materials, sterile gloves, single-use disposable needles, syringes or lancing devices, and sufficient laboratory sample tubes.
- Post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP) – Instruct on proper procedures in the case of accidental exposure, including keeping a register of incidents.
- Avoiding contaminated phlebotomy equipment – Reusing tourniquets and finger-prick devices should be avoided. Common-use items should be thoroughly cleaned, hand hygiene should be strictly practiced, and single-use items should not be reused.
- Patient cooperation – Teach students how to clearly communicate with patients about their procedure, either through written or verbal information.
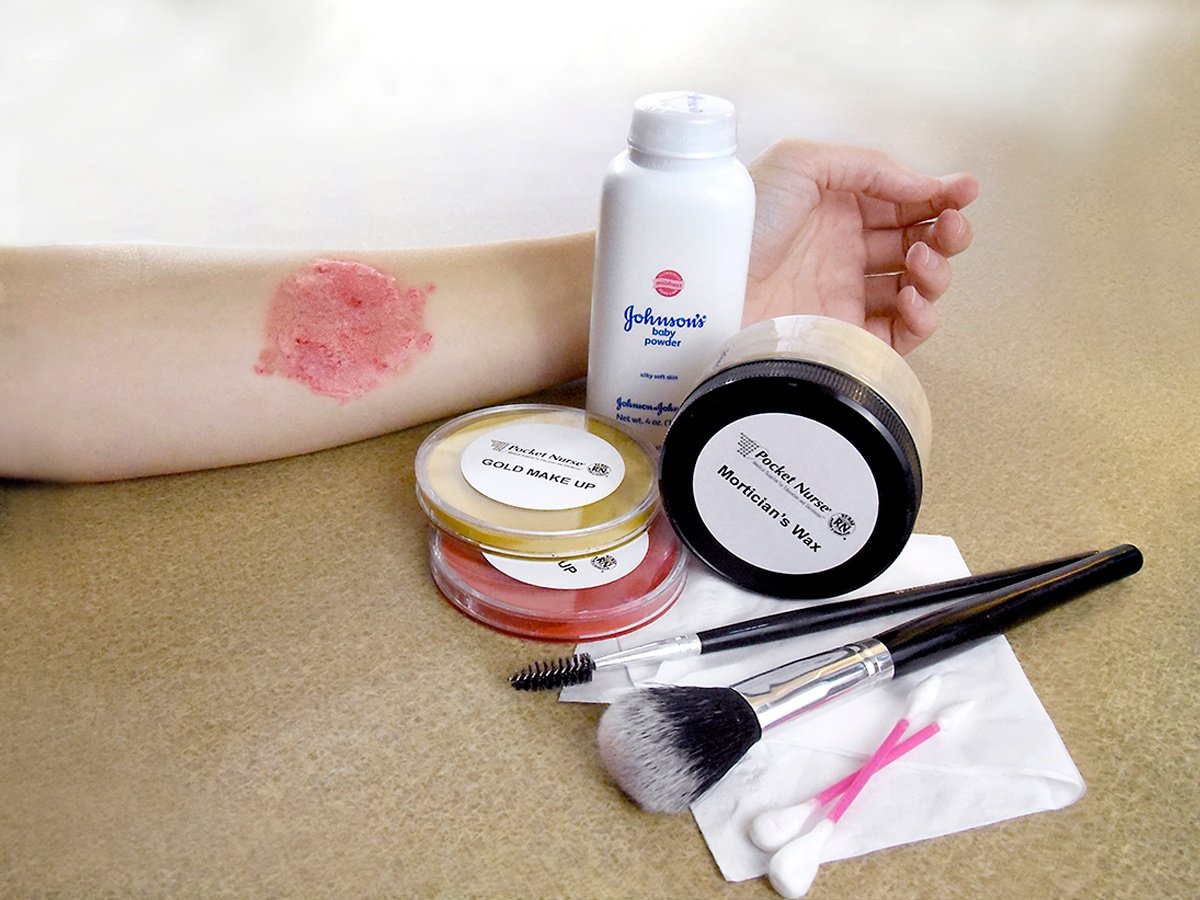
Pocket Nurse offers a predesigned phlebotomy kit for students to learn the complex procedure of drawing and collecting blood. It includes a convenient caddy to hold the necessary supplies to develop best practices.
Source: WHO Guidelines on Drawing Blood: Best Practices in Phlebotomy