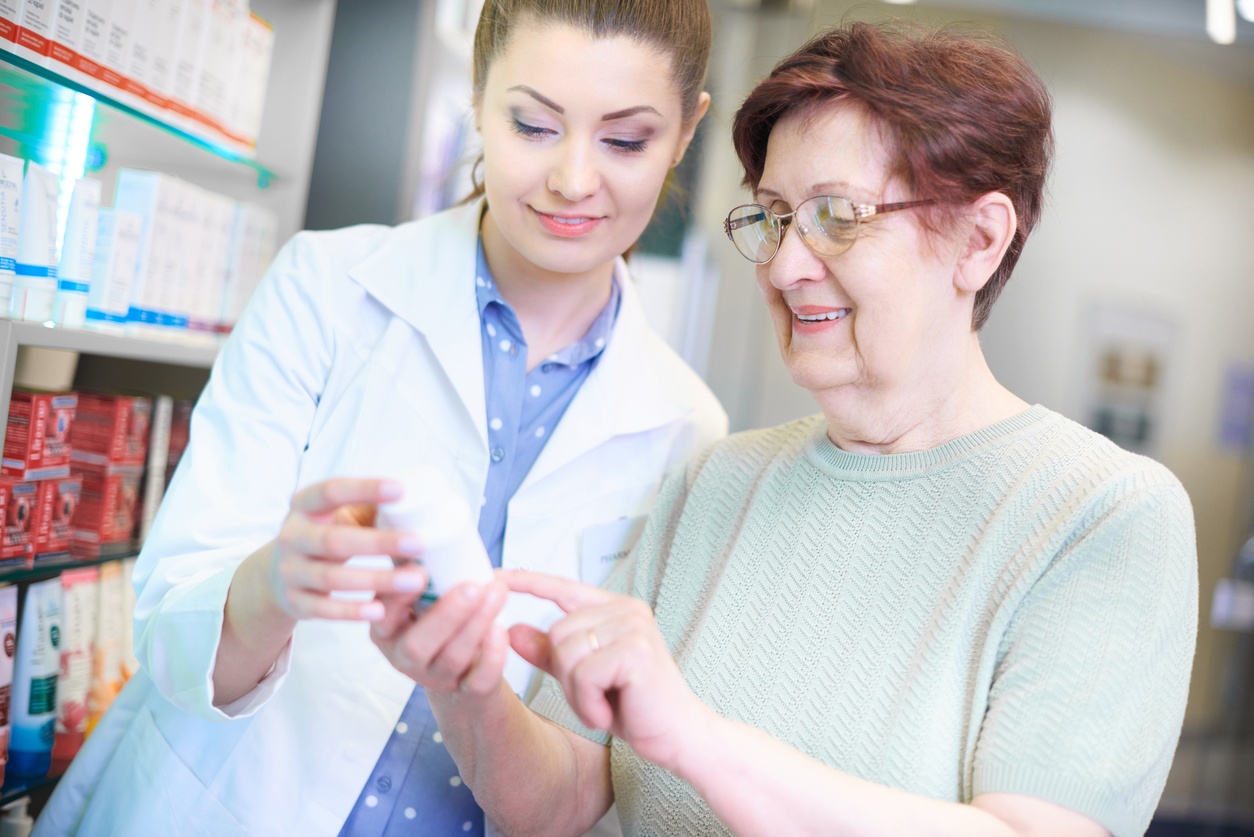
Pharmacists used to be the medication authorities in white lab coats who dispensed relief from behind high counters. They were seldom called on to interact with patients. For that matter, they seldom collaborated with other health care providers; it was a very segmented industry, with doctors handing out orders, and patients expected to follow them without question.
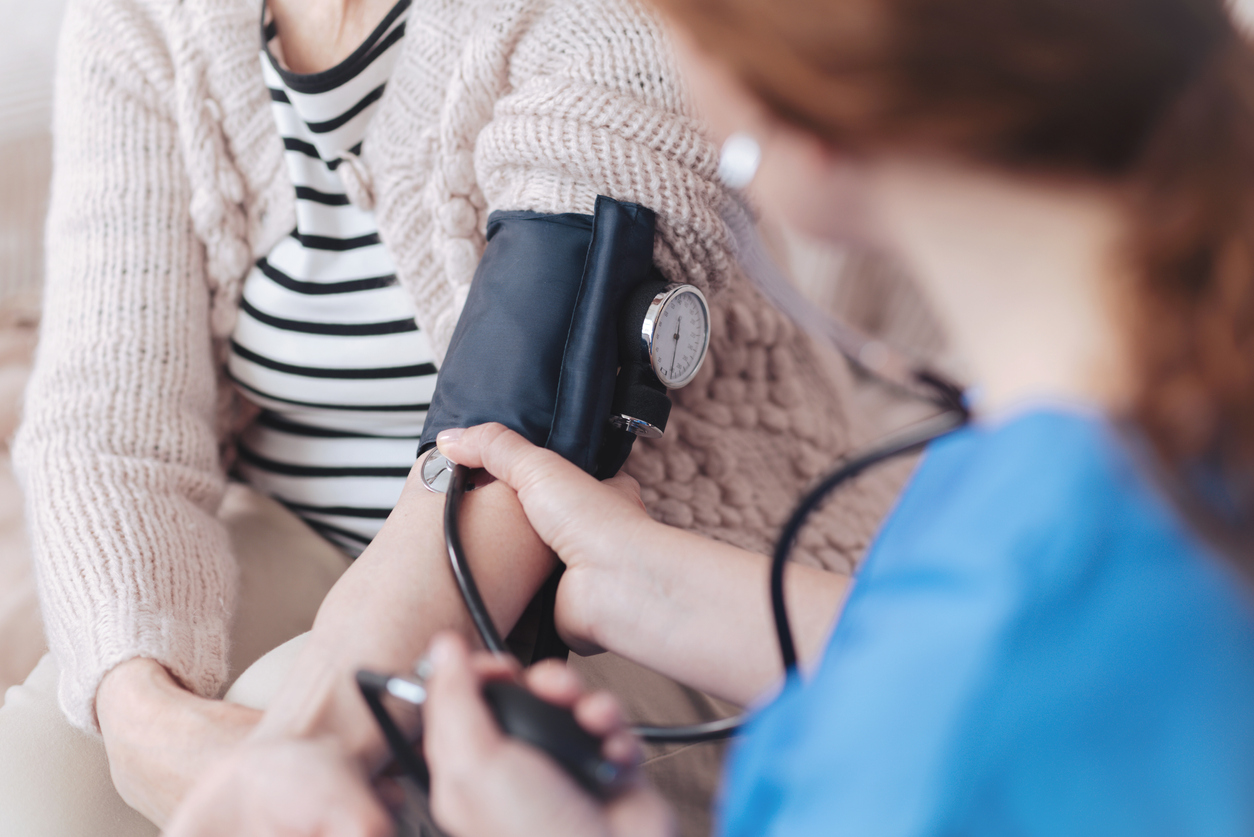
As technology has progressed and health care has changed, pharmacists are coming out from behind those high counters and providing direct care and counseling to patients. Instead of simply dispensing medications, they are often depended on to dispense medical guidance, healthcare advice, and preventative care. Pharmacists, pharm techs, nurses, and doctors work collaboratively with each other and with patients instead of dictating from on high.
3 Reasons Pharmacy Roles Have Changed
1. Advances in Technology
Technology changes have enabled more and better treatment options, as well as provided ways to coordinate care across healthcare providers and institutions.
2. Changes in the Healthcare Model
Consumers are calling for better access to low-cost, convenient health care. Pharmacies can meet this demand by providing high-quality and cost effective preventative screenings and immunization services. Pharmacies have become a vital link for health care, providing counseling, medication therapy management, and identifying potential drug interactions.
3. An Emphasis on Patient-Centered Care
With advances in technology and changes to the way health care is handled in America, patients and payors are focused on cost reduction and improved patient outcomes. Patients are more involved in their healthcare decisions, demanding transparency in care and increased access to healthcare information.
Pharmacist-led programs ease care transitions by:
- Reducing the occurrence of adverse drug events
- Addressing medication adherence
- Lowering hospital readmission rates
One study even found that medication reconciliation programs, which is when pharmacists review patients’ medication regimens and provide adherence counseling, reduced the risk of hospital readmission by 50 percent.
How Simulation Can Help in these New Roles
As pharmacy education continues to evolve, innovative active learning is called for to enhance pharmacotherapeutic knowledge and clinical skills. The Accreditation Council on Pharmacy Education (ACPE) has approved the use of simulation for up to 60 hours (20 percent) of the 300-hour experiential education requirement.
Simulation-based pharmacy education:
- Enhances students’ fundamental knowledge
- Improves learner confidence
- Enhances clinical performance
- Stimulates critical thinking
- Decreases medication administration errors
Pharm Ed™ from Pocket Nurse® is a subset of pharmacy education and pharm tech solutions created to support simulation-based pharmacy education.
Sources:
“The Role of Pharmacists in a Changing Health Care Environment,” CVSHealth.com
“Patient Simulation in Pharmacy Education,” American Journal of Pharmaceutical Education