Diabetes is a serious, complex, chronic condition that affects more than 30 million people in the United States, which is equivalent to 1 in 10 Americans. The strong correlation between diabetes, heart disease, and stroke makes it a condition that must be taken seriously.
Diabetes is a tough diagnosis to be given, and although there are many medications, treatment regimens, and resources available, it requires attention, time, lifestyle changes, and strict management in order for the disease to not become a life-threatening condition.
Diabetes mellitus disturbs the way the body turns food into energy to fuel essential physiologic functions. In healthy individuals, the pancreas makes an adequate amount of insulin. Insulin is the hormone that allows cells to utilize sugar for energy. Diabetics’ ability to produce or respond to the hormone insulin is impaired, leaving an excess of sugar outside the cells and in the bloodstream. This results in abnormal metabolism of carbohydrates and elevated levels of glucose in the blood and in the urine. High levels of sugar in the bloodstream lead to serious health conditions.
There are three major types of diabetes: Type 1 diabetes, Type 2 diabetes, and gestational diabetes.
Type 1 diabetes is also called insulin-dependent diabetes. It used to be referred to as juvenile-onset diabetes, because it often begins in childhood. It is an autoimmune condition and is caused by the body attacking its own pancreas with antibodies. In Type 1 diabetes, the damaged pancreas doesn't make insulin.
Type 2 diabetes, the most common form of diabetes, accounts for 95 percent of adult diabetes cases. An estimated 26 million American adults have been diagnosed with this disease. Type 2 diabetes used to be referred to as adult-onset diabetes, but with the obesity epidemic, more teens are now developing Type 2 diabetes. It is also referred to as non-insulin-dependent diabetes and is frequently a milder form of diabetes than Type 1. However, it can still cause health complications in the smallest blood vessels in the body that perfuse the kidneys, nerves, and eyes. This type of diabetes also increases your risk of heart disease and stroke.
In Type 2 diabetes, the pancreas usually produces some insulin. But either the amount produced does not meet the body's needs, or the body's cells are resistant to it.
Gestational diabetes is a condition that is triggered by pregnancy. It is often diagnosed the second or third trimester of pregnancy. Because high blood sugar levels in a mother are circulated through the placenta to the baby, gestational diabetes must be controlled to protect fetal growth and development.
The reported rate of gestational diabetes is between 2 to 10 percent of pregnancies according to the National Institutes of Health. Gestational diabetes usually resolves after pregnancy. Having gestational diabetes does, however, put mothers at risk for developing Type 2 diabetes later in life.
November is Diabetes Education Month, which makes it a perfect time to share Pocket Nurse’s diabetes educational solutions. With the alarming statistics available, we take the disease seriously and are committed to offering a variety of educational solutions for the simulation lab and classroom.
Pocket Nurse Diabetes Education Solutions
- The Diabetes Skills Training Kit: This kit offers a comprehensive selection of product solutions to teach students to practice typical diabetes-related care scenarios. It includes a blood glucose monitoring system (glucometer), test meter strips, control solution, lancets, Demo Dose® Insuln Bundle, Demo Dose Glucagn kit, Insulin syringes with Needles, Protein/Glucose/Ketone Chem Strips, an Inject-Ed™, Alcohol Prep Pads and Non-Latex Exam Gloves.
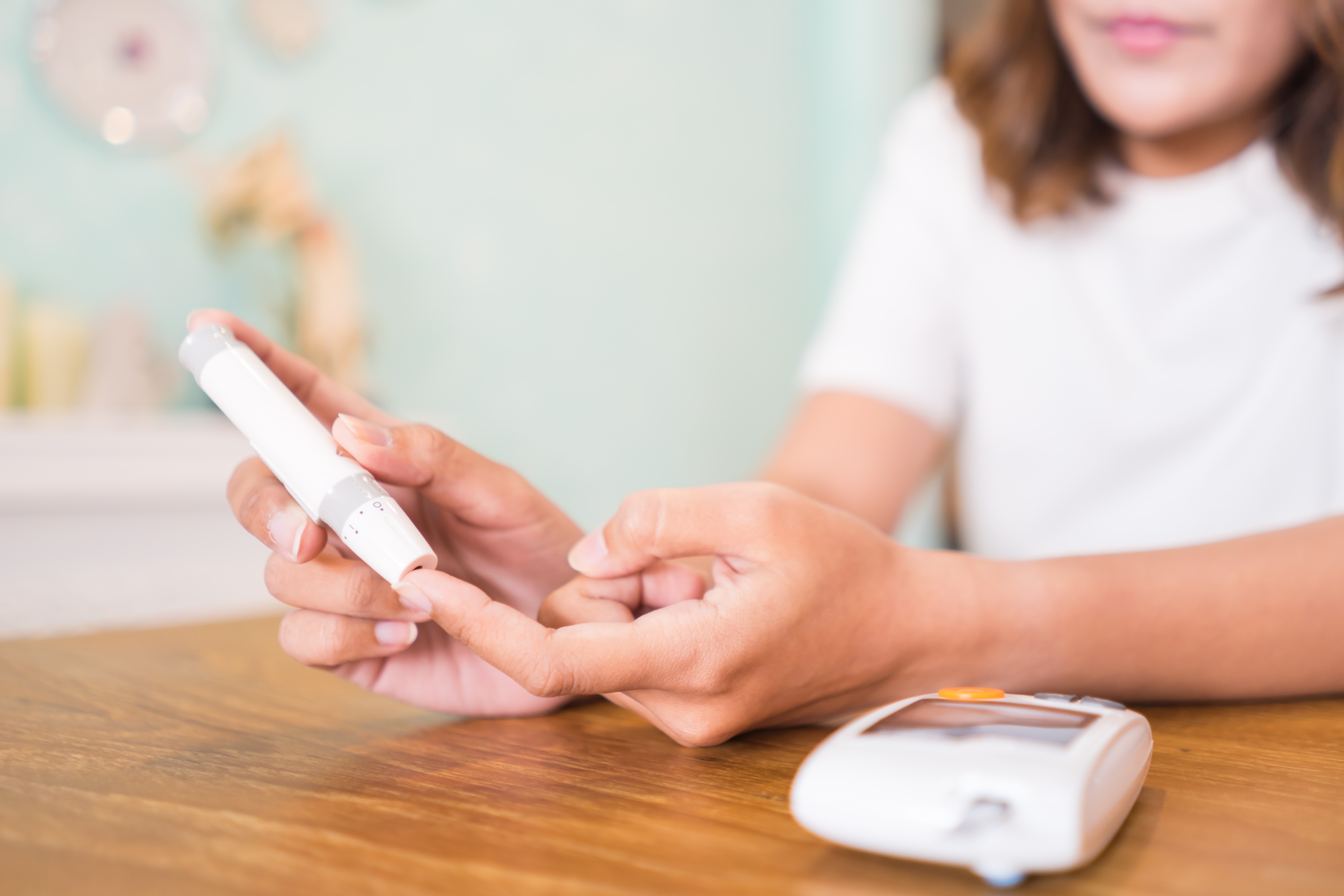
- Glucometers: A glucometer provides capillary blood sugar readings by detecting the level of glucose (sugar) in a person's blood. Pocket Nurse offers a variety of glucometers, also known as blood glucose meters, and their compatible test strips and control solutions. New this year is a simulated glucometer, the GlucoSim, which allows the instructor to program a blood glucose reading for a student to react and respond to.
- SA FingerStick Kit: This overlay finger model can be placed over the thumb or fingers of standardized participants or manikins for practicing finger sticks to test capillary blood sugars with a glucometer. Recipes are provided to prepare low, normal, and high-blood glucose solutions. An injection port allows refilling of the finger overlay.
- Models: Pocket Nurse offers a realistic Diabetic Foot Model and a Type II Diabetes Mini Model that both depict visual representation of how this disease can effect body parts and organs in advanced stages.
- Demo Dose Insuln Bundle: This bundle includes six vials of different types of simulated insulin for educating students on proper techniques in preparing and administering insulin injections.
- Insulin Syringes: Insulin syringes are an essential component in the process of preparing simulated insulin for injection. Pocket Nurse offers multiple insulin syringe options to assist you with educating your students on proper technique for preparing and administering simulated insulin in your scenarios and classroom using 30-, 50- ,100-unit syringes.
- Insulin Pen/Cartridges/Needles: Our universal pen and cartridge permits students to practice preparing insulin dosages in a pen/cartridge preparation as students learn to adjust dosages and change the pen needle for each injection.
- Insulin Comparison Chart: This chart provides a quick-look guide on the different types and dosages of insulin for diabetes management.
- Anatomical Charts: Understanding Type 1 and Understanding Type 2 Diabetes anatomical charts make great additions to a classroom and simulation lab for use when educating students on the differences between the two types of diabetes.
- Demo Dose Glucagn Kit: This is a realistic glucagn emergency kit for use in low-blood-sugar scenarios.
- Injection Belly: This soft stomach replica is an invaluable tool for teaching students how to properly inject insulin into the subcutaneous tissue in the abdominal area.
- Monofilament Diabetic Foot Test: This tool allows instructors to teach students how to identify those at risk of developing neuropathy or diabetic foot ulcers.
- Demo Dose Oral Medications: Pocket Nurse offers several oral medications commonly taken by diabetics that can be used in your simulation scenarios. For example, we offer: Glucophag, Metformn, Glucotrl and Diabet.
Beth Telesz, MSN, RN, is the Corporate Nurse Educator at Pocket Nurse. She can be reached at btelesz@pocketnurse.com, or see our Ask-A-Nurse feature at PocketNurse.com.
Sources:
WebMD.com, “What causes a lack of insulin in patients with Type 2 diabetes"