Diabetes is either Type 1 or Type 2, both of which can be managed with insulin therapy. In addition, Type 2 diabetes can be managed through lifestyle changes, such as losing weight and eating healthfully.
In Type 1 diabetes, the pancreas doesn’t make enough insulin. Type 1 diabetes is a chronic disease that is usually diagnosed in childhood; it used to be called juvenile diabetes. Type 1 diabetes is managed through insulin therapy.
In Type 2 diabetes, formerly referred to as adult-onset diabetes, the body becomes resistant to the insulin it is producing. This leads to the body not being able to regulate blood glucose levels, and can be brought on by many factors including being overweight, a lack of physical activity, and age.
What Does Insulin Do?
Insulin is a type of hormone, which is secreted by the pancreas. Insulin has a two-fold purpose:
- Regulate sugar in the bloodstream
- Store excess glucose for energy
After eating, carbohydrates in food are broken down into glucose, which is a type of sugar that is meant to be used as a source of energy. Glucose enters the bloodstream, and in response, the pancreas produces insulin to keep the blood-sugar levels within a normal range. Excess glucose is stored in the liver, which releases glucose into the blood to maintain normal blood sugar levels.
In diabetes, the body doesn’t produce enough insulin or is unable to use the insulin it is producing. This results in high levels of glucose in the blood because it cannot enter the cells. If left untreated, these high glucose levels can damage organs and nerves in the body, leading to blindness, kidney failure, or neuropathy.
Insulin therapy helps replace insulin in Type 1 diabetes, and can be used in Type 2 or gestational diabetes, which occurs during pregnancy if other therapies cannot regulate blood glucose.
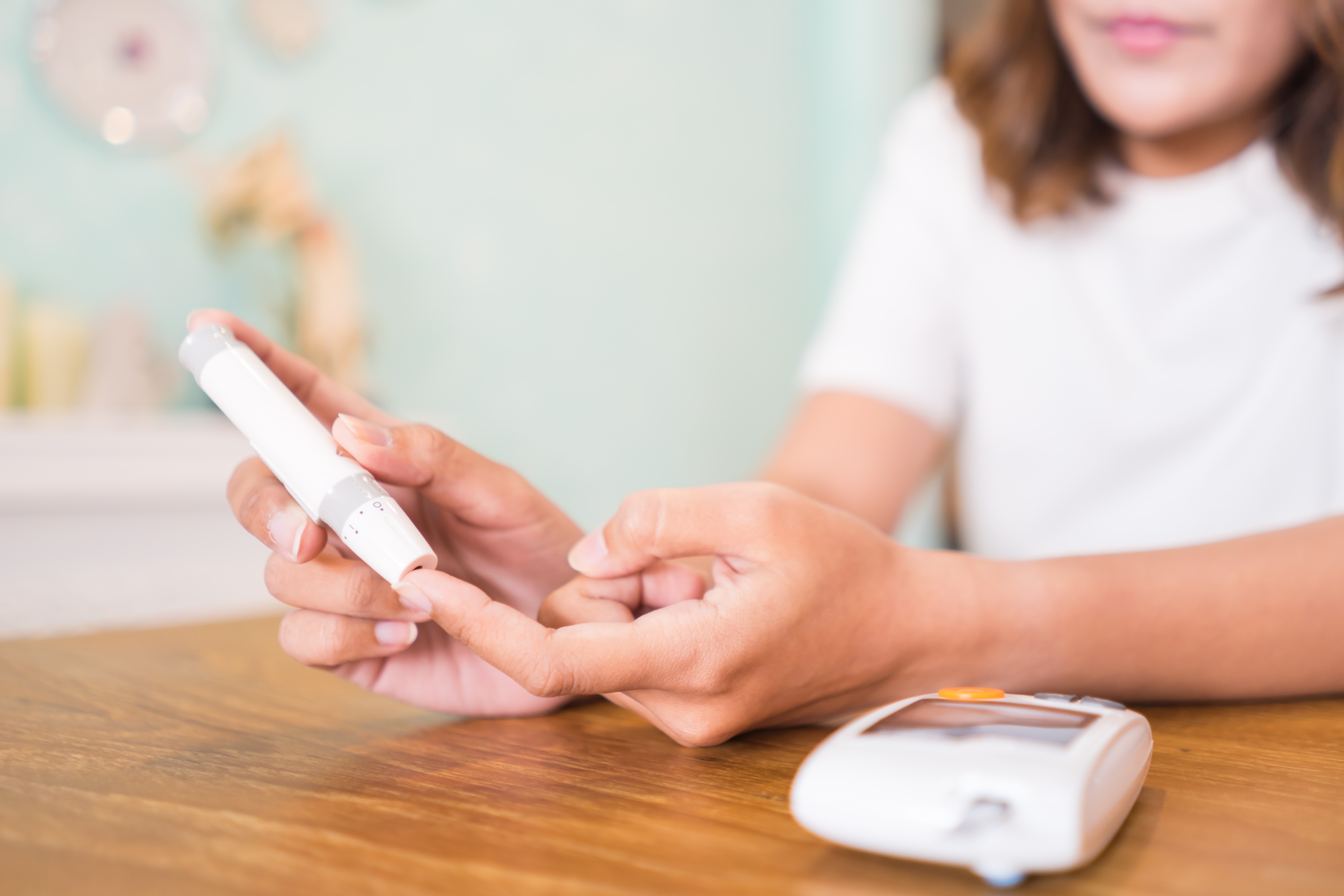
Several types of insulin are available, and a patient’s dose will depend on his or her needs. Insulin types vary in how quickly and how long they can control blood sugar. Some types of insulin are combined with other types. Insulin is delivered under the skin via injection, insulin pen, or insulin pump.
Pocket Nurse features a comparison chart listing types of insulin, how quickly they take effect, duration of efficacy and more details. It makes a good reference guide for the classroom or study guide for nursing students. We also offer an insulin pen and cartridges to teach proper insulin administration.