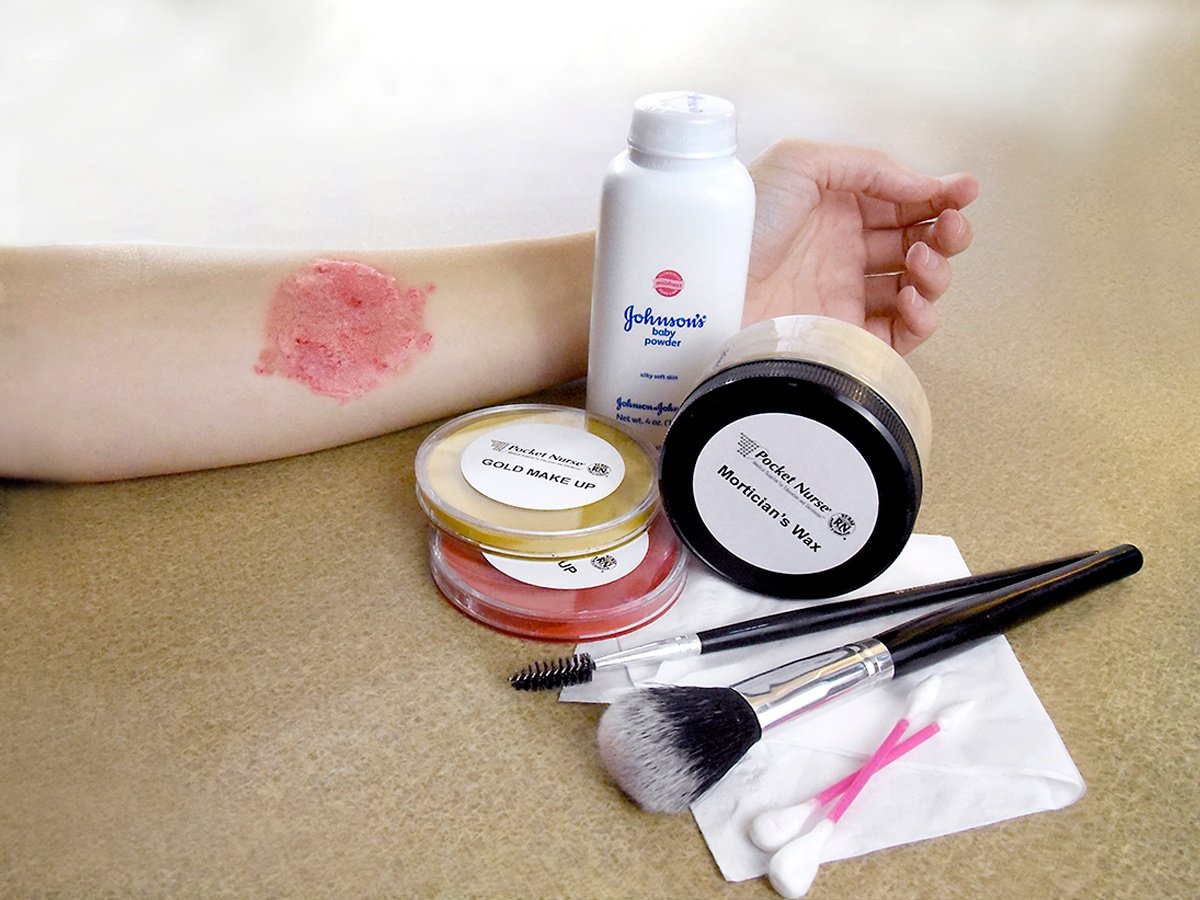
Insect bites are prevalent this time of the year, with many people enjoying time engaging in outdoor activities, increased travel, and relaxation outside. Bug repellant sprays are commonly used to reduce the risk of bug bites.
Insects most often bite to protect themselves or their nests. Some insects, such as fleas, bite to feed. In many cases, the bug bites cause no pain or irritation. Sometimes, swelling, itchiness, or a red welt may develop at the site of the bite. Ice or a cold pack wrapped in a thin towel is routinely recommended to reduce swelling and itching that is minimal. The majority of bites do not cause illness, and the swelling, itching, and redness go away without intervention. An infection may result, however, if the bite is scratched and skin is broken.
If medical attention is sought, the doctor may prescribe over-the-counter (OTC) medications to help relieve symptoms that are not severe. Package directions for use should always be followed. If the bite becomes infected, antibiotics will be prescribed to be taken by mouth or applied to the skin.
General Information and Recommendations for Insect Bites
- Bite symptoms typically fade away within a week or two.
- Avoid scratching or picking at the bite to help prevent infection.
- Apply ice or a cold pack wrapped in a thin towel to help relieve itching.
- Avoid hot baths or showers as these may make itching worse.
- OTC anti-itch medications may be considered for non-severe bites (ask your pharmacist or doctor for a recommendation for your condition).
- Contact a licensed pest-control professional if you suspect you have insects in your home for direction on safe insect removal.
- If you received medical attention, follow up with your doctor as advised.
In addition, a person may have a severe allergic reaction to a bug bite or sting, with a notable example being a bee sting allergy causing anaphylaxis shock. In the case of a severe allergic reaction, call 9-1-1.
Get prompt medical attention if the patient’s condition changes, advanced symptoms such as severe swelling or pus appear, or you have additional questions and concerns. If something doesn’t feel right, contact your healthcare provider.
Pocket Nurse solutions for educating on reaction to bug bites include an Epi-Pen trainer and Demo Dose® simulated antibiotics. To educate students on basic insect bite care, see our Patient Care and Infection Control in our current Simulation and Healthcare Education catalog or at www.pocketnurse.com
Beth Telesz is the Corporate Nurse Educator for Pocket Nurse.
*Disclaimer: Pocket Nurse is not liable for any self-treatments or care provided; these are general care guidelines for non-emergent/non-severe/non-complicated insect bites to follow at your own risk. Get prompt medical treatment as needed. Pocket Nurse is not a healthcare provider or prescriber. Demo Dose is for instructional use only, not for human or animal use.