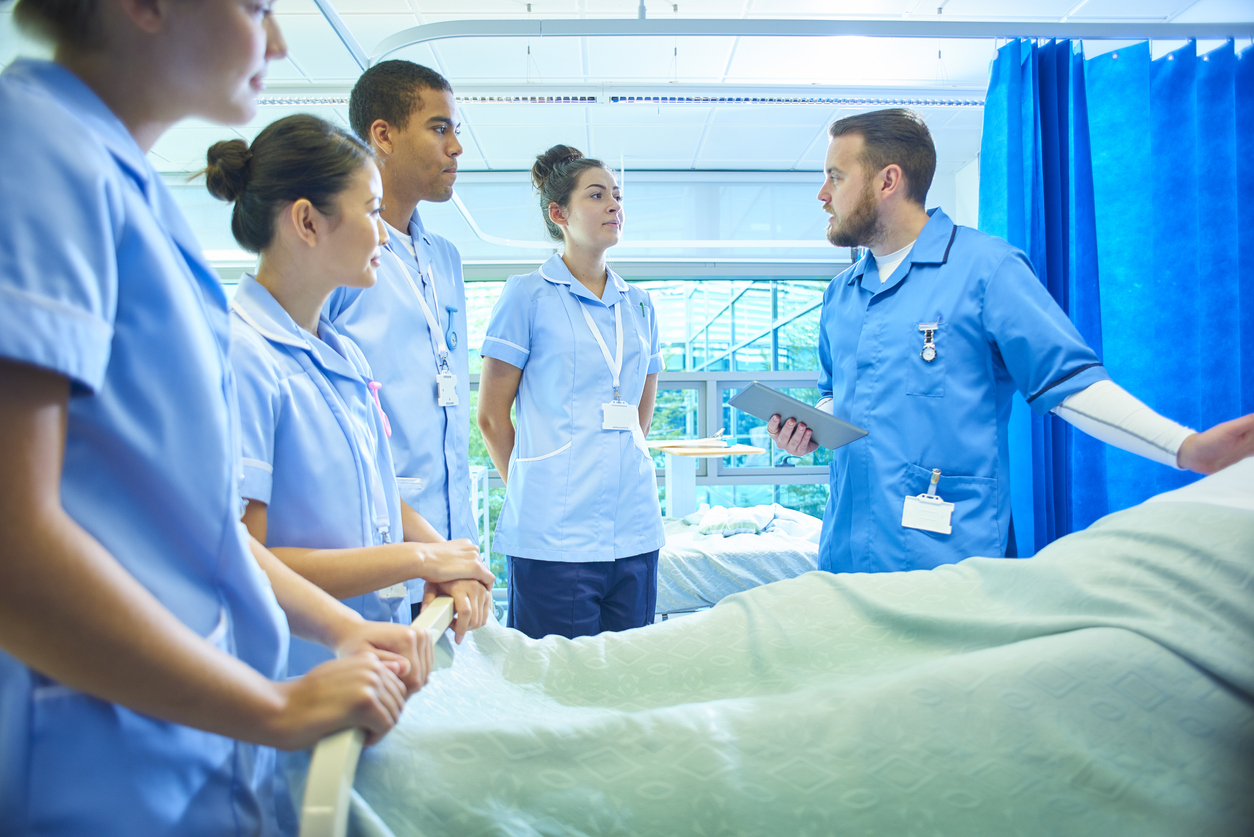
Simulation “refers to an artificial representation of a real world process to achieve educational goals through experiential learning.”1 Last week’s post, “Simulation in Healthcare Education,” delved into the definition of simulation in a healthcare setting and its four ...
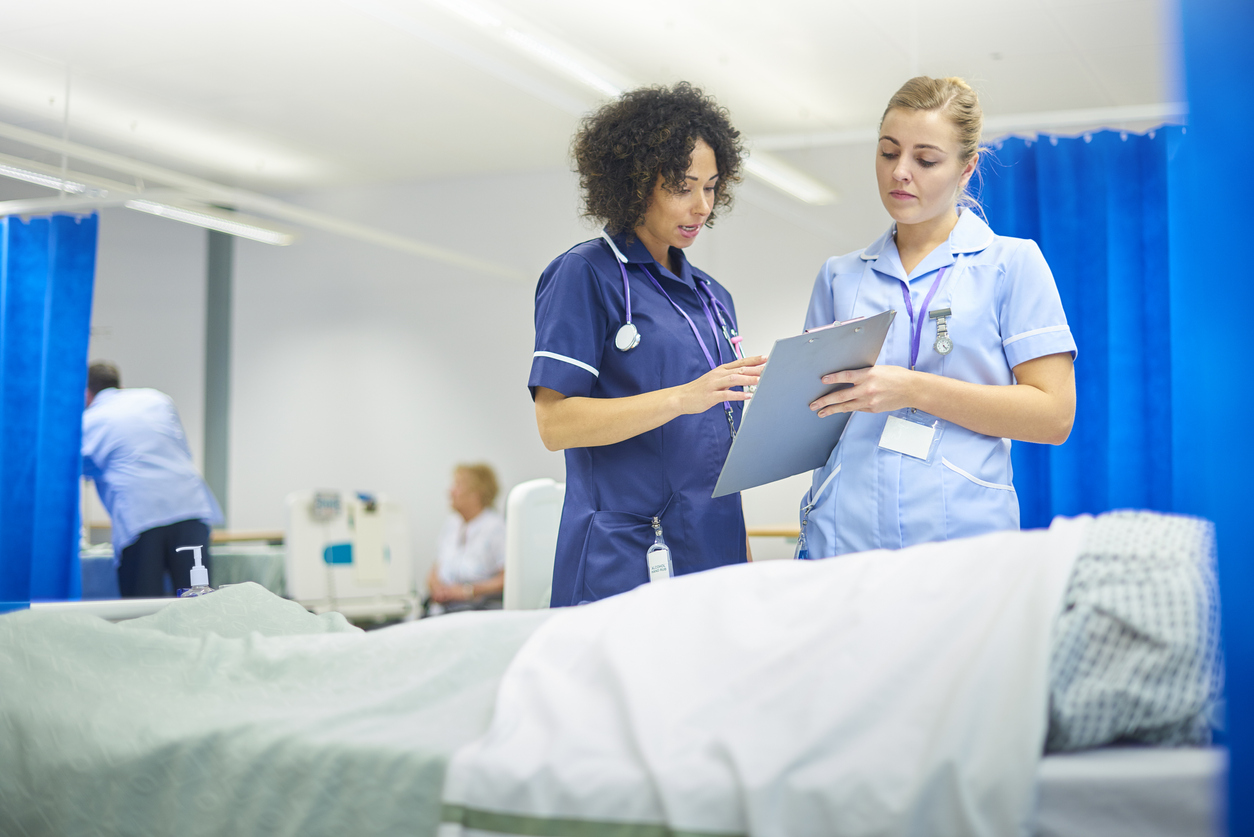

According to the Society for Simulation in Healthcare (SSIH), simulation education is “the bridge between classroom learning and real-life clinical experience.” (From the SSH About page.) Healthcare simulation, in particular, has four main purposes: Education, assessment, research, and system integration.

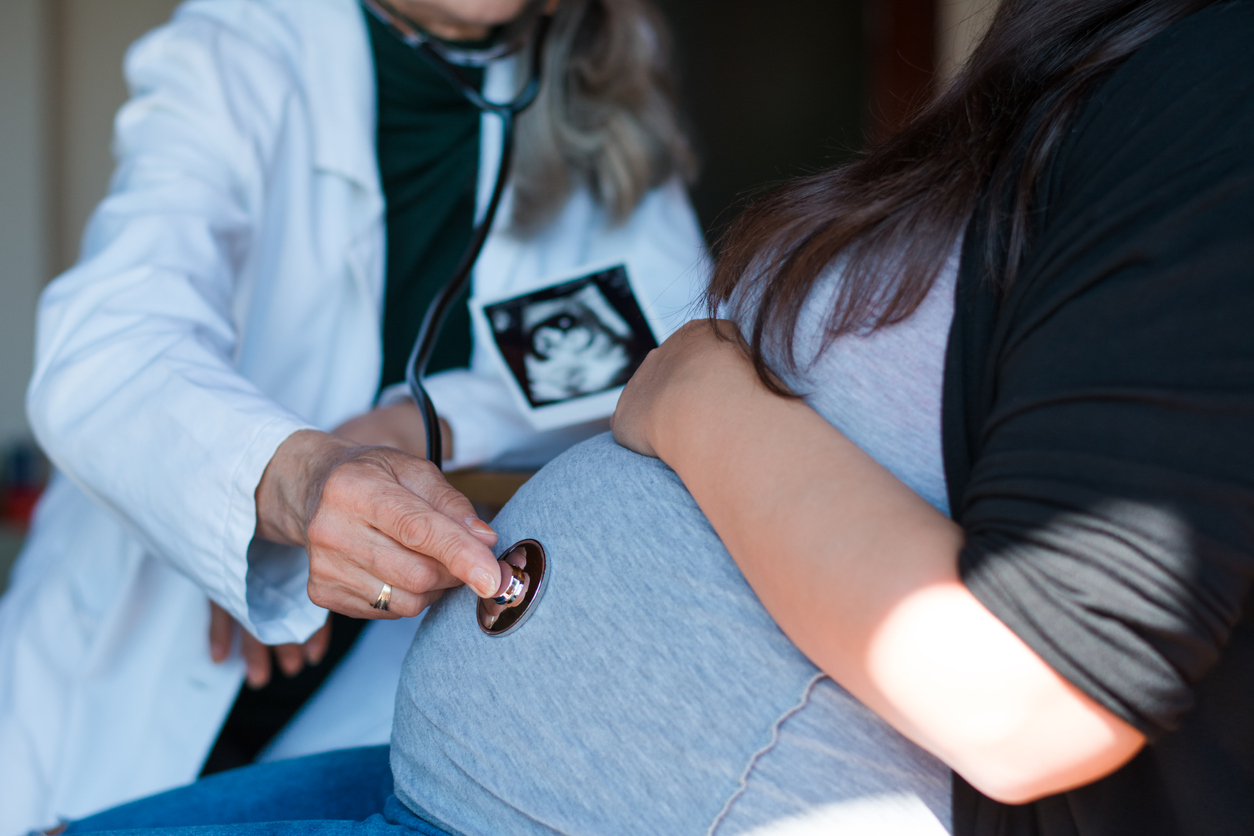
The United States is the only developed country in the world where the rate of maternal death is rising. From 1987 to 2015 (the latest year for which numbers are available), the number of reported pregnancy-related deaths has steadily increased from 7.2 per 100,000 live births to 17.2 deaths per 100,000 live births.1
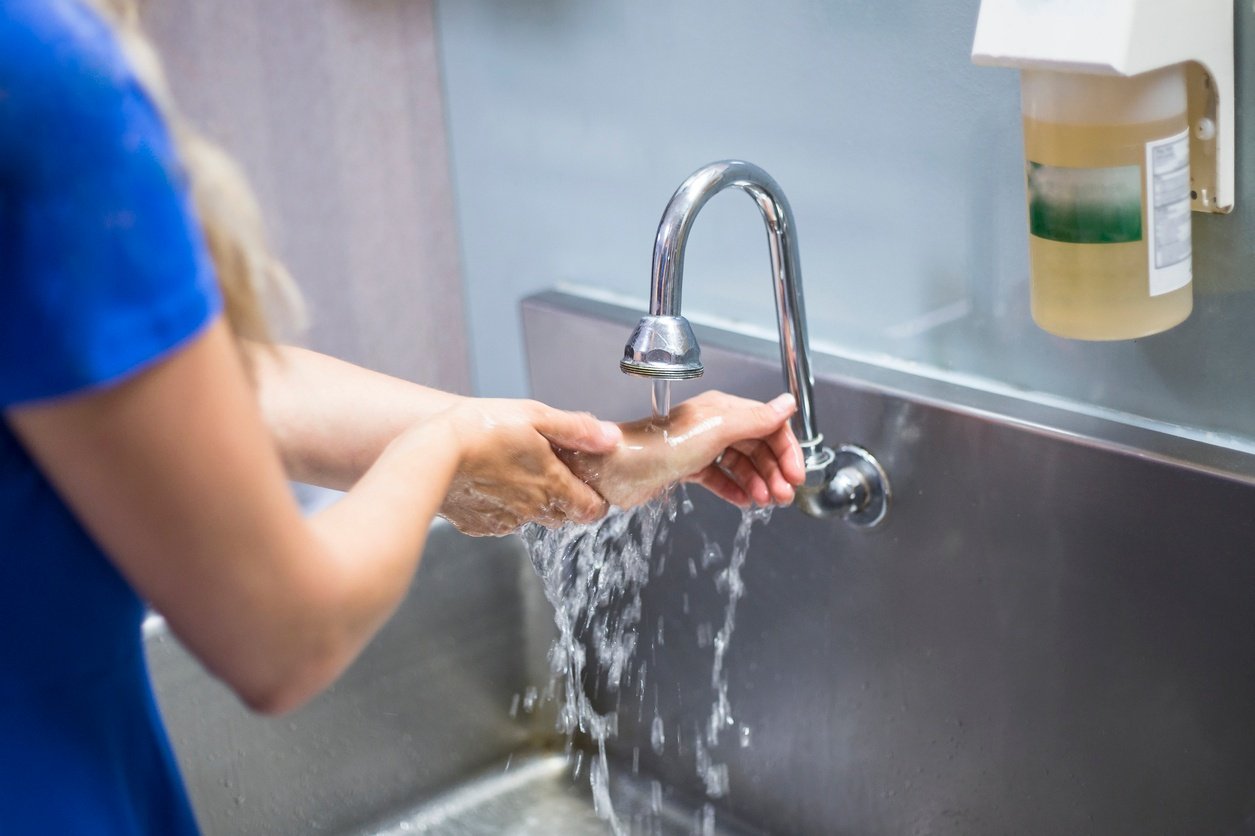

Through my experience as a nurse assistant, hand washing was always emphasized: when I entered a hospital room, before I touched a patient, after I touched a patient, and when exiting the room. I completely understood the hand-washing protocol and I did it eagerly, but others did not.

During some recent water cooler office talk, a few co-workers were sharing some experiences of buying big-ticket household items. One had purchased a very expensive refrigerator, another bought a TV, and I had recently bought a sofa from an online retailer. Coincidentally, we all had issues that needed handled after the sale; two of us did not have the ...